Last Updated
How Do You See the World if You Have Astigmatism?
Home / LASIK for Astigmatism /
Last Updated
Imagine trying to decipher the world through a lens that’s not quite clear, where lines seem wavy, and lights seem to have a radiant glow or streak. Objects, both near and far, may appear blurred or slightly distorted. Nighttime might bring added challenges, with bright lights like those from oncoming vehicles or streetlamps appearing to stretch out in varying directions. This is a glimpse into the world of someone with astigmatism, an eye condition where an irregular corneal shape alters the usual clarity of vision, making the world seem a tad out of focus.
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error that affects how the eye bends light and causes blurriness, so the images you are looking at appear fuzzy and unclear. Most people have this condition to some degree, but there are widely different levels of severity.
If astigmatism is making it hard to see clearly, there are treatment options. Corrective lenses are the most common treatment. You may also qualify for LASIK surgery for astigmatism.
How Does Astigmatism Affect the Eyes?
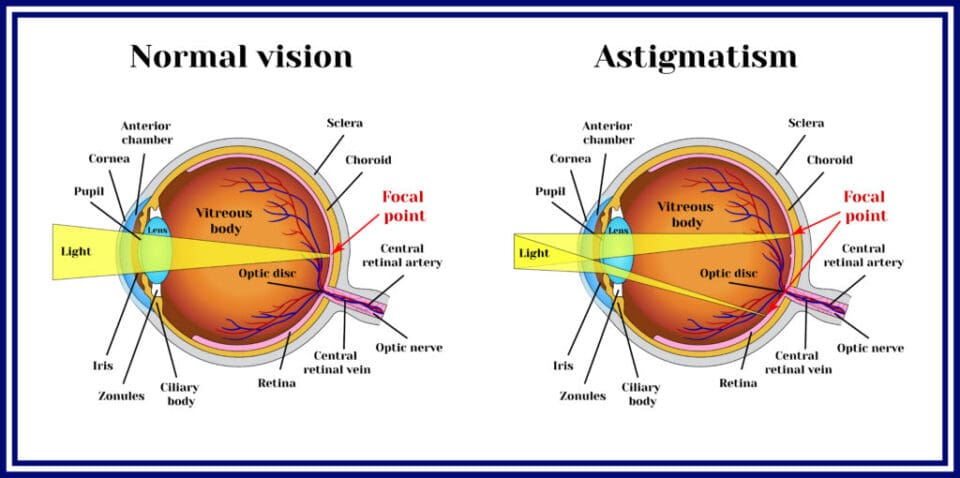
Astigmatism is a common eye condition that affects the way light enters the eye, leading to blurry or distorted vision. Unlike a healthy eye with a round cornea (the clear front surface of the eye), in astigmatism, the cornea is shaped more like a football or an egg, with varying degrees of curvature.
The irregular corneal shape causes light rays to be refracted, or bent, unevenly as they enter the eye. As a result, the light does not focus properly on the retina, which is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Instead of forming a single, clear image, the light focuses on multiple points on the retina, leading to blurred or distorted vision.
Astigmatism can affect the eyes in various ways, leading to difficulties and symptoms such as:
- Difficulty seeing objects at various distances.
- Trouble reading fine print, seeing clearly at night, or even noticing subtle details in their surroundings.
- Eye strain, headaches, and squinting as the eyes work harder to focus and compensate for the irregular corneal shape.
Fortunately, astigmatism can be corrected with the use of eyeglasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery. These methods help to adjust the way light enters the eye, compensating for the corneal irregularity and allowing for clearer vision. Regular eye examinations are important to detect and correct astigmatism early on, ensuring optimal eye health and visual acuity.
How Does Astigmatism Impact Vision?

Astigmatism leads to distorted or blurry vision at far and near distances.
Light focuses on multiple points instead of just one. At night when looking at lights, they appear to bounce off their primary location. For example, when looking at a stop light, the actual light appears fuzzy, and the light seems to reflect off it in multiple directions.
When looking at an object, it appears blurry and unclear. It has an abnormal softness and fuzziness to it. The edges of the object may appear undefined.
Astigmatism Types
There are three astigmatism types.
- Hyperopic astigmatism: If both or one principal meridian is farsighted, someone has hyperopic astigmatism.
- Myopic astigmatism: If both or one principal meridian is nearsighted, someone has myopic astigmatism.
- Mixed astigmatism: If one principal meridian is farsighted and the other one is nearsighted, someone has mixed astigmatism.
The different types of astigmatism don’t generally result in different effects or signs. The differences in visual acuity come down more to the severity of the astigmatism and the severity of vision issues accompanying it.
Once someone is diagnosed with astigmatism, it is classified as irregular or regular. The principal meridians are not perpendicular with the irregular type, but they are perpendicular with the regular type. In most cases, astigmatism is the regular type affecting the cornea.
Why corneal shape differs among people remains unknown. However, there is likely an inherited element to the condition. In some cases, it can develop following an eye injury, disease, or surgery.
What Are the Different Levels of Severity?
The severity of astigmatism is stated in diopters.
A diopter is a unit of measurement of the optical power of a lens. Essentially, diopter strength references the power of a lens. A high diopter number means your vision is worse, or requires more correction.
The severity of an astigmatism is correlated to the diopter number.
- Mild astigmatism: less than 1.00 diopters
- Moderate astigmatism: 1.00 to 2.00 diopters
- Severe astigmatism: 2.00 to 3.00 diopters
- Moderate astigmatism: more than 3.00 diopters
To determine if someone has astigmatism, the doctor typically performs a comprehensive dilated eye examination. They will also ask about any vision changes. This can help the doctor to determine if the symptoms are associated with astigmatism.
Astigmatism Treatment Options

When astigmatism is slight, people often do not need treatment. However, when it is impacting vision, a comprehensive eye examination is needed to get a definitive diagnosis. From here, the doctor can determine which treatment is appropriate to improve vision.
Corrective lenses are commonly prescribed to people who have astigmatism. They work by counteracting a cornea or lens curvature. Eyeglasses for astigmatism have lenses that compensate for the corneal abnormality.
Contact lenses can also be used for astigmatism. They come in a variety of styles and types.
- Disposable soft
- Rigid, gas permeable
- Extended wear
- Bifocal
Contact lenses are also used as part of the orthokeratology procedure. For this procedure, the doctor has the patient wear rigid contact lenses. They are worn for many hours a day. The purpose is to even out the curvature of the eyes. Once the curvature is evened out, people still need to wear their lenses to maintain the new shape, but they can wear them less frequently.
If someone stops wearing their contact lenses after this procedure, the curvature correction does dissipate, and the cornea eventually reverts back to its abnormal shape. Because of this, people have to wear the lenses long term to maintain the benefits of the procedure.
There are four types of refractive surgery that can be used for astigmatism.
- LASIK: This works to sculpt the corneal shape so light properly focuses in the eye. It involves making a flap in the cornea and replacing the flap after using a laser for the reshaping.
- PRK: This procedure involves removing the epithelium and then changing the corneal shape using a laser.
- LASEK: LASEK is similar to PRK, but the epithelium is not removed. The doctor uses it to create a flap and then puts it back into place after using the laser to reshape the cornea.
- Epi-LASIK: This procedure is a variation of LASEK. The epithelium is separated using a blade instead of alcohol, and a laser then reshapes the cornea.
References
- Eye Health Statistics. American Academy of Ophthalmology.
- Astigmatism. American Optometric Association.
- What Is Astigmatism? American Academy of Ophthalmology.
- Facts About Astigmatism. National Eye Institute
- Astigmatism. Mayo Clinic.
- Influence of Different Types of Astigmatism on Visual Acuity. (Jul–Sep 2017). Journal of Optometry.
The information provided on this page should not be used in place of information provided by a doctor or specialist. To learn more, read our Privacy Policy and Editorial Policy pages.