Do Omega-3s (& Fish Oil) Impact or Improve Eyesight?
Home / How Diet Impacts Eye Health & Vision /
Last Updated:
Omega-3 fatty acids are often discussed for their ability to decrease inflammation. They contain certain components that may deliver a variety of health benefits.
Table of Contents
While you usually hear about these acids in regard to heart health, there is some evidence to show that they may promote eye health in children. Other research looks at the potential advantages for age-related eye issues.
The best way to get this nutrient is from diet. You can then get a more diverse panel of nutrients that may work with omega-3 fatty acids to bring greater eye health benefits.
Another option is to take them in supplement form. It’s imperative that the supplement has the right dose and is high in quality.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?

Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of nutrient. These are fats the body does not produce naturally, so people have to acquire them via their diet. In the last 30 to 40 years, scientists have discovered numerous potential benefits associated with these healthy fats.
Cell membranes throughout the body use these fatty acids, and they are integral to their proper formation. They also play an important role in the membrane’s cell receptor function.
Omega-3 fatty acids are in the polyunsaturated fat family. The three primary ones include:
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which is generally used for energy.
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which is the body’s most important omega-3 fatty acid. It is a major structural component of various body parts.
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), which is partially converted into DHA. It also has other roles in the body.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids & the Eyes
This nutrient may contribute to better eye health. DHA is especially helpful since there are high levels of it present in the retina of the eye.
Several studies have looked at how this nutrient may impact vision development in infants. Analysis of multiple studies concluded that preterm infants who were provided formula that was supplemented with DHA had far greater visual acuity when they were 2 to 4 months old. These results were compared to preterm infants who did not receive an omega-3 supplement with their formula.
You deserve clear vision. We can help.
With 135+ locations and over 2.5 million procedures performed, our board-certified eye surgeons deliver results you can trust.
Your journey to better vision starts here.
Other research looked at the potential benefits of this nutrient for dry eyes. Some research suggests that a supplement of omega-3 fatty acids could reduce symptoms of this condition. It may help to alleviate dry eye symptoms, such as stinging, burning, and itching.
Some research suggests that DHA can promote better eye health. One study stated that if someone is not getting enough of this omega-3 fatty acid, they have a higher risk of vision problems.
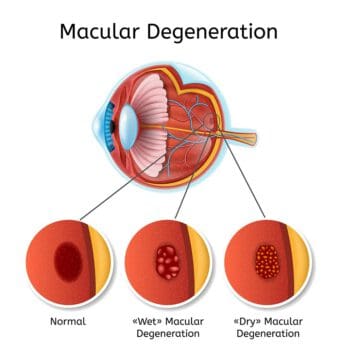
Other possible benefits of omega-3 fatty acids relate to macular degeneration. Getting enough of this nutrient may reduce a person’s risk of developing this eye condition.
Some studies in 2008 and 2009 looked at the role of omega-3s and macular degeneration. One showed that this nutrient appeared to reduce the risk of the development of wet macular degeneration. Another showed a 30 percent reduction in the risk of developing macular degeneration among people with the highest intake of this nutrient via their diet.
What Foods Are High in This Nutrient?
Most people get adequate omega-3 fatty acids from their diet. The foods rich in this nutrient are diverse, so it is relatively easy to get enough via diet. The following foods contain high levels of omega-3 fatty acids:
- Mackerel
- Cod liver oil
- Salmon
- Oysters
- Herring
- Sardines
- Caviar
- Anchovies
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseeds
- Walnuts
- Soybeans
- Algae and seaweed
- Kidney beans
Incorporating these foods into your regular diet helps to ensure that you are getting enough of this nutrient. Ideally, aim to eat at least one of these foods every day.
Taking an Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplement

If you don’t get enough of these fatty acids from your diet, you might consider taking a supplement. It is important to talk to your doctor first to ensure that the supplement you choose is high in quality. Ideally, the supplement should contain all three types of omega-3 fatty acids.
In the United States, a lot of foods are fortified with these fatty acids, so the average person does not need to take a supplement. You shouldn’t take in more than 3 grams per day of omega-3s. Taking too much may cause uncomfortable symptoms that affect the gastrointestinal system.
The following are possible side effects of these supplements:
- Fishy aftertaste
- Indigestion
- Loose stools
- Bad breath
- Nausea
- Rash
People who take blood-thinning medications should avoid these supplements unless a doctor says it is okay to take them. Using omega-3 supplements with these types of medications carries an increased risk of bleeding. This was generally observed among people taking more than 3 grams of omega-3s per day.
You deserve clear vision. We can help.
With 135+ locations and over 2.5 million procedures performed, our board-certified eye surgeons deliver results you can trust.
Your journey to better vision starts here.
Additional Benefits of Taking Omega-3s or Fish Oil
Omega-3 fatty acids, including EPA, DHA and ALA, have proved beneficial for several aspects of ocular health. The primary benefits are the lowering of risk factors for heart disease and the ability of omega-3s to help stave off inflammation in joints throughout the body.
- Improve Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease
- Researchers documented in numerous studies that communities of people that consume higher quantities of fish have lower rates of heart disease. This observation has been attributed to omega-3 fatty acids.
- Omega-3s help reduce triglycerides, lower blood pressure and increase good HDL cholesterol levels. They also help prevent the formation of blood clots and plaques.
- Helps Combat Inflammation
- Chronic or long-term can pose a serious threat to your health. Omega-3 fatty acids help fight inflammation by impeding the production of certain inflammatory agents such as cytokines and eicosanoids.
- Omega-3s may also aid in slowing autoimmune diseases, boosting mental health, easing rheumatoid arthritis, strokes, infant development and metabolic ailments.
What Are Potential Side Effects of Omega-3?
Just because fish oil has health benefits doesn’t mean more is better. High doses of omega-3 supplements can lead to a host of adverse effects.
Some of these side effects may show up even at lower doses. It is for this reason that you are advised to consult your health caregiver before taking supplements. Below are some of the potential side effects.
- Diarrhea
- Diarrhea is among the most common side effects of taking omega-3 supplements, especially in high doses. Fish oil and flaxseed oil are the common supplements to take to ease constipation, but too much leads to diarrhea.
- Doctors recommend that you take any supplements with meals and decrease your dosage if this symptom persists.
- Nausea
- Nausea is a common side effect of numerous treatments and supplements. This is also the case with fish oil. Some approaches that may help with nausea:
- Take the fish oil in small, divided doses with your meals.
- Refrigerate the fish oil. This helps reduce the aftertaste and prevent it from becoming rancid (another major cause of nausea).
- Buy enteric-coated fish. It is less likely to have an aftertaste.
- Nausea is a common side effect of numerous treatments and supplements. This is also the case with fish oil. Some approaches that may help with nausea:
- Risk of Bleeding
- Easy bruising and risk of bleeding are much less common side effects. They may occur when you take high doses of omega-3 fatty acids combined with anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs such as coumadin (warfarin) and Plavix (clopidogrel).
- Acid Reflux and Indigestion
- Because of the high-fat content of fish oil, some people may experience acid reflux characterized by belching, heartburn and stomach discomfort. It may also trigger indigestion. You can reduce the chances of this occurrence or relieve the symptoms by lowering doses and taking supplements with meals.
- Other Side Effects
- Other notable side effects of omega-3s that can present include:
- Unpleasant breath
- Unusual body odor
- Allergic reactions (uncommon)
- Insomnia
- Vitamin A toxicity
- Low blood pressure
- Other notable side effects of omega-3s that can present include:
You deserve clear vision. We can help.
With 135+ locations and over 2.5 million procedures performed, our board-certified eye surgeons deliver results you can trust.
Your journey to better vision starts here.
References
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: An Essential Contribution. Harvard School of Public Health.
- Fish Oil. (October 2017). Mayo Clinic.
- What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids? (December 2018). Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids. (November 2018). National Institutes of Health.
- Eye Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids. All About Vision.
- Fish Oil Supplements and Dry Eyes. (November 2017). Mayo Clinic.
- The Role of Omega-3 Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Health and Disease of the Retina. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research.
- Circulating Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science.
- Historical overview of omega-3s and heart disease. (June 2008). National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- Omega-3 supplement effects on triglycerides in diabetic patients. (March-April 2008). National Library of Medicine.
- Reduction of blood pressure through fatty fish consumption. (February 2010). National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammation. (June 2006). National Library of Medicine.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids. (June 2021). StatPearls.
This content is for informational purposes only. It may have been reviewed by a licensed physician, but is not intended to serve as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider with any health concerns. For more, read our Privacy Policy and Editorial Policy.
